AutoNom
AutoNom
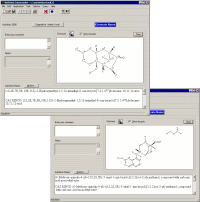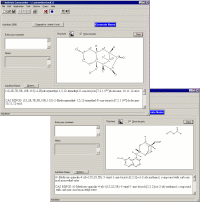
AutoNom (Automatic Nomenclature) is a chemical-name-generating program that assigns systematic IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) chemical names to drawn structures in seconds.
For more information see AutoNom.
MDL Information Systems provides two versions of AutoNom:
- AutoNom Standard is free of charge and can be downloaded via the Beilstein homepage, or accessed via Chemweb. AutoNom Standard is also included on each ISIS 2.4 CD.
- AutoNom 2000 includes stereochmistry, supports CAS ring system naming, and has the ability to number atom locants within named structures.
ISIS/Draw and ISIS/Base have now functions that allow you to name structures automatically. This works with AutoNom Standard and AutoNom 2000.
AutoNom: Fast, Reliable
Chemical Naming
Save Time and Gain Consistency The nomenclature rules proposed by IUPAC are crucial to helping scientists communicate information about chemical compounds. Unfortunately, the rules are complex and often open to interpretation by individual scientists. Algorithmic chemical naming not only collects together all of these rules, but uniformly applies them. Developers at MDL Information Systems GmbH have teamed with IUPAC to create software algorithms for automatically implementing IUPAC rules from electronically drawn chemical structures. With the program, scientists can focus on performing syntheses rather than on becoming nomenclature experts. And organizations ensure that each compound synthesized is accurately and consistently named-a requirement for registering and ultimately mining chemical data. In fact, AutoNom is specified and used by the Beilstein Institute, one of the oldest and most respected indexers of organic chemistry, to manage all of its chemical naming tasks. AutoNom approaches nomenclature like a nomenclature specialist. Using a structure from ISIS/Draw or the Beilstein Structure Editor, AutoNom
Key Features in AutoNom 2000
System Requirements AutoNom 2000 runs on Intel or Intel-compatible PCs running Microsoft Windows 95, 98, or NT 4.x. It requires 8 MB RAM and 5 MB hard disk space. AutoNom 2000 can be implemented as a desktop application. In addition, AutoNom 2000 TT provides the interface code as a DLL to allow customized installations, such as running in batch mode for naming large quantities of compounds. To find out why AutoNom has been popular with chemists for over a decade, download AutoNom Standard (included in the Beilstein Commander) or try a free web implementation of AutoNom on ChemWeb. With AutoNom Standard, an unrestricted free version, you can test it's speed and accuracy. If you are interested in pricing or would like to order AutoNom 2000, please click here.
|
|
|